What Is NVIDIA DLSS?
Video games are becoming far more graphically detailed and environmentally complex than ever before. These vast strides in visual fidelity are made possible in part due to new rendering processes such as ray-tracing, which provides real-time reflections, lighting, and shadows that are far more lifelike than what we're used to seeing in our games – appearing more like movies than something you'd play on a console.
That said, these graphical leaps require additional processing power. So much processing power, in some cases, that it's impractical or even impossible to run them on contemporary hardware without some much-needed assistance. That's where artificial intelligence, or AI, comes into play.
NVIDIA, famous for its powerful graphics cards as well as its recent strides in AI deep learning technology, has introduced a process called DLSS, or Deep Learning Super Sampling. On compatible hardware, DLSS negates the need for traditional anti-aliasing techniques such as TAA or MSAA (which have historically been used to make game graphics look less jaggedy, but at a major performance cost).
What is NVIDIA DLSS?
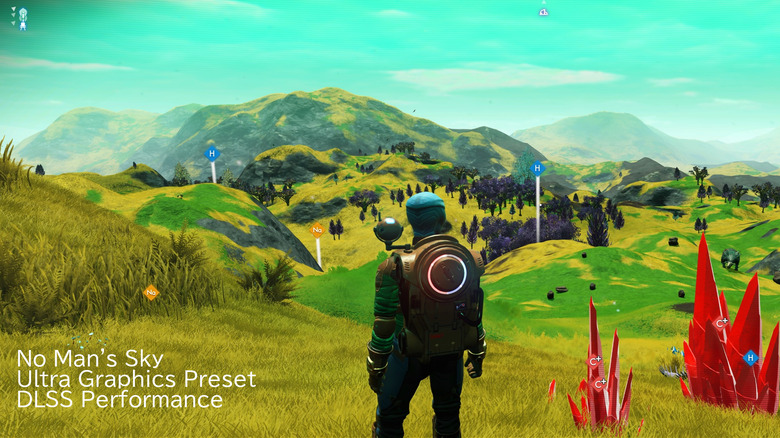
NVIDIA DLSS stands for Deep Learning Super Sampling (via NVIDIA), and it's essentially an added graphical processing layer that developers can insert into their games. Given that you have compatible hardware, such as the RTX 2060 or RTX 3060 Ti graphics cards, you can flip the DLSS setting in any DLSS-compatible video game, like "Doom Eternal" or "No Man's Sky," though it's not compatible with just any game. You'll generally find DLSS in newer games where developers have deliberately added support.
DLSS generally comes in different flavors. But this will differ between games, depending on how DLSS has been implemented. You can usually pick a different level of quality based on how far you're comfortable downscaling your base image before DLSS upscales it back to your preferred resolution. For instance, Performance-grade DLSS generally downscales your image the most, whereas Quality-grade DLSS downscales it the least. It's always worth testing different combinations of DLSS with other graphical settings to get the best result.
How does NVIDIA DLSS work?
NVIDIA's Deep Learning Super Sampling basically tells a dedicated part of your RTX graphics card (20-series and above) to process an image and scale it up to your preferred resolution. It's able to do this by way of AI deep learning techniques that see a lower-resolution image and know what it's supposed to look like when scaled up to a higher resolution.
In this sense, NVIDIA DLSS takes the pressure off your video card and processor to output a high-resolution image with all of the bells and whistles (like ray-tracing) turned on. By using NVIDIA DLSS, you can theoretically turn all of your graphics settings to maximum, while only experiencing a negligible hit to your performance and graphical fidelity.
Some theorists predict that future consoles, such as a Nintendo Switch Pro model, could include DLSS capabilities built in to support 4K resolutions while retaining the system's handheld design. No such model has been confirmed, but it's within the realm of possibility.
NVIDIA DLSS pros and cons
DLSS has only gotten better with time, and its 2.0 release made it far more viable for gaming. It's reasonable to expect that whatever additions DLSS 3.0 brings will improve the process even more. Its biggest pro is that it makes certain games far more accessible on older or less powerful hardware, driving down the potential cost to build a PC gaming-ready computer if you want to play the latest and greatest video games.
That said, it isn't without its downsides. Based on how it's implemented, DLSS might not be powerful enough to make ray-tracing viable on a PC that isn't equipped with a high-powered RTX 3070 video card (or above) if you'd like to play games at 1440p resolutions or higher while maintaining 60 frames per second. In some cases, such as in "Battlefield V", DLSS is known for making the image look fuzzy, though it's worth noting that that game used DLSS 1.0 rather than the far smoother DLSS 2.0.
NVIDIA DLSS is compatible with any RTX 20-series video card or above. Due to microchip shortages driving up the costs of all video cards, you're not likely to find a much better deal than the RTX 3060, which offers a balanced price to performance ratio and costs around $650 to start, though it depends on which retailer you choose.